
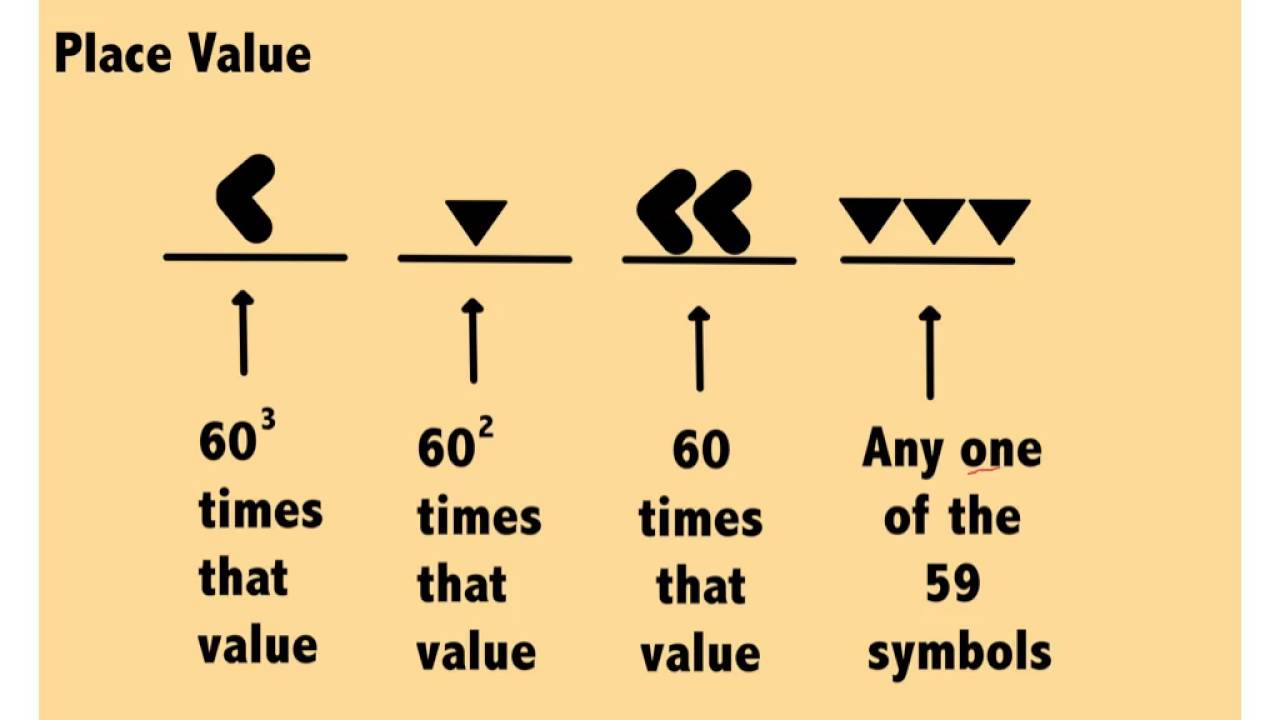
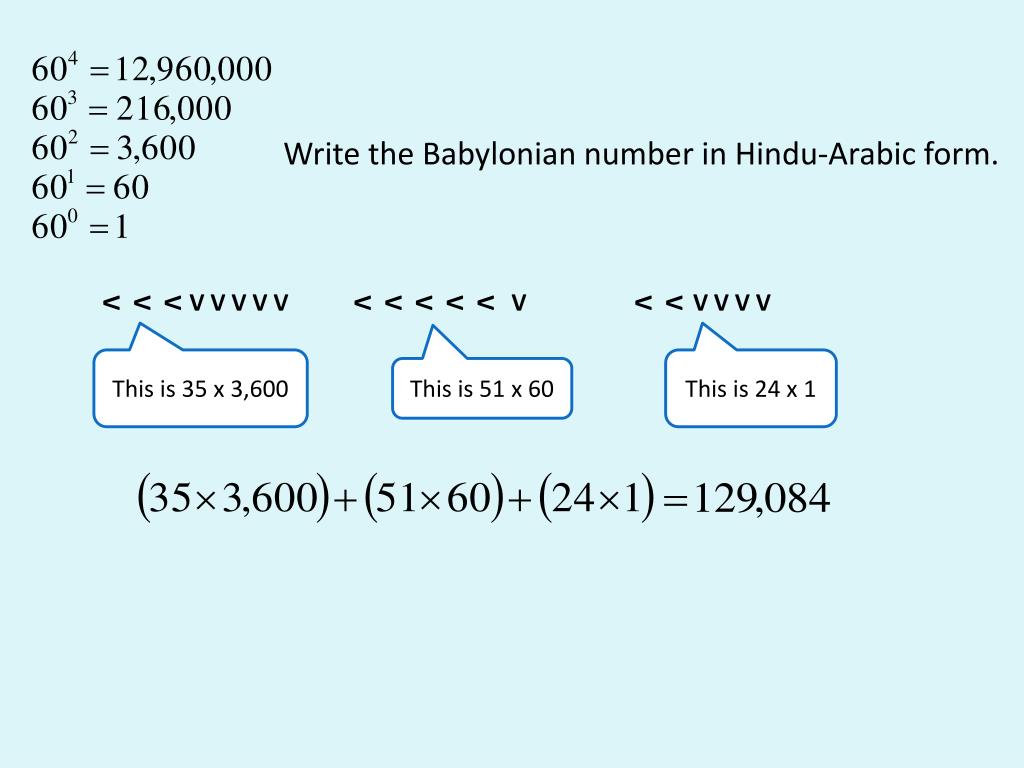
Understand and Convert Babylonian Numerals to Hindu-Arabic Numerals In this section, we explore how the Babylonians, Mayans, and Romans addressed these issues. No matter the system, the issues of representing multiple values and how many symbols to use had to be addressed. However, as societies became more complex, as commerce arose, as military bodies developed, so did the need for a system to handle large numbers. This can even be seen in our use of the term few, which is an inexact quantity that most would agree means more than two. For example, a shepherd likely didn't manage more than 100 sheep, so quantities larger than 100 might never have been encountered. But it might not be useful to know the difference between 145 and 167, as those quantities never had a practical use. In nearly all societies, knowing the difference between one and two would be useful. These differences arose due to cultural differences.
The system used in Australia would necessarily differ from the system developed in Babylon that would, in turn, differ from the system developed in sub-Saharan Africa. Understand and convert between Roman numerals and Hindu-Arabic numerals.Įach culture throughout history had to develop its own method of counting and recording quantity.Understand and convert Mayan numerals to Hindu-Arabic numerals.Understand and convert Babylonian numerals to Hindu-Arabic numerals.(credit: modification of work by Osama Shukir Muhammed Amin FRCP(Glasg), CC BY 4.0 International) Learning ObjectivesĪfter completing this section, you should be able to: Figure 4.3 Babylonians used clay tablets for writing and record keeping.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
